Dental Implant Surgery
The dental implant surgery typically involves the following steps:
-
- Evaluation: The patient undergoes a thorough evaluation, including X-rays and dental impressions, to determine the optimal location and placement of the implants.
- Implant placement: The oral surgeon makes an incision in the gum tissue to expose the jawbone and prepares a small hole in the bone to receive the implant. The implant is then inserted into the hole and the gum tissue is sutured closed.
- Healing: Over the next several months, the implant fuses with the surrounding bone in a process called osseointegration, providing a stable base for the dental prosthesis.
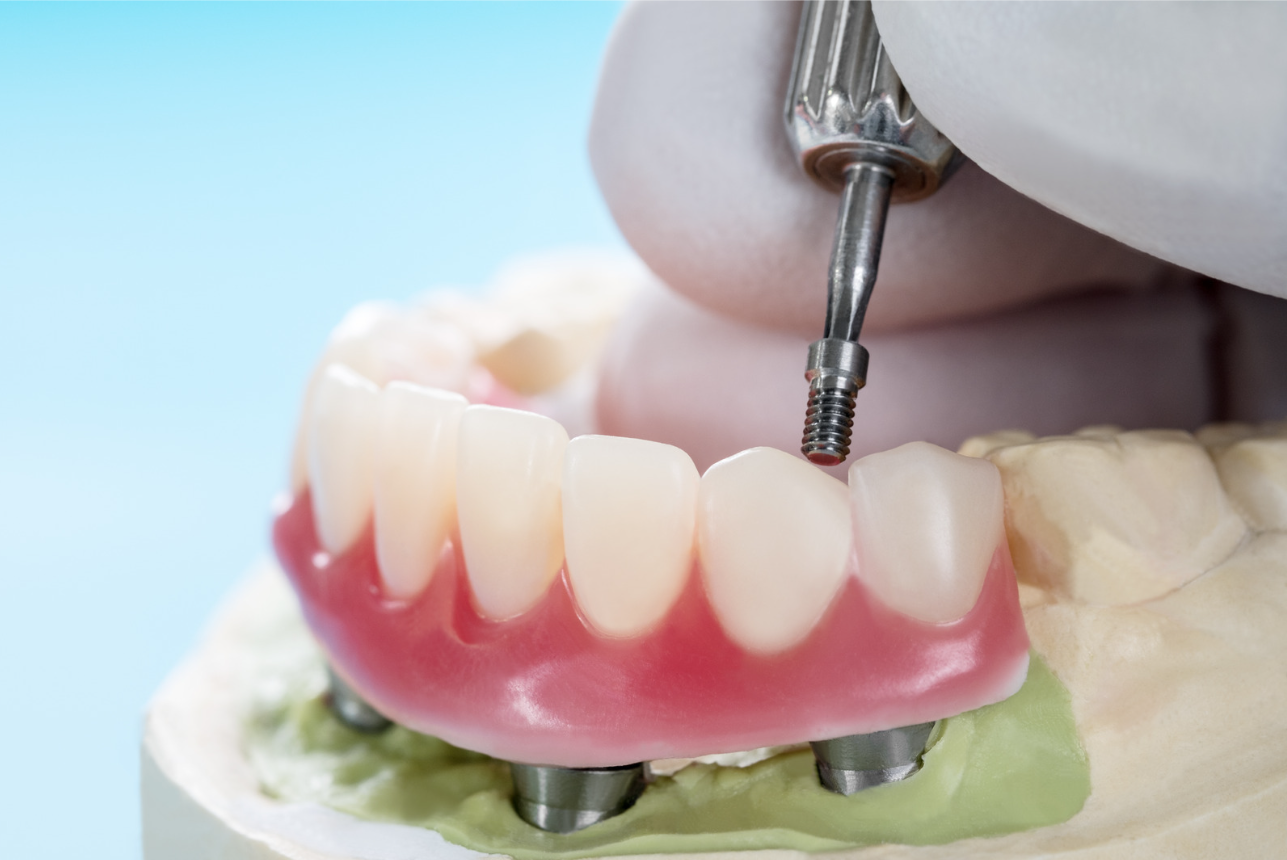
- Abutment placement: After the implant has fully fused with the bone, an abutment (a small connector piece) is attached to the implant to provide a secure attachment point for the dental prosthesis.
- Prosthesis attachment: Finally, a dental prosthesis, such as a crown, bridge, or denture, is custom-fabricated and attached to the abutment.
However, the procedure can be costly and time-consuming, and not all patients are good candidates for implant surgery. Your dentist or oral surgeon can provide guidance on whether dental implant surgery is the right choice for your individual needs and can help you prepare for and maintain your treatment.